Introduction
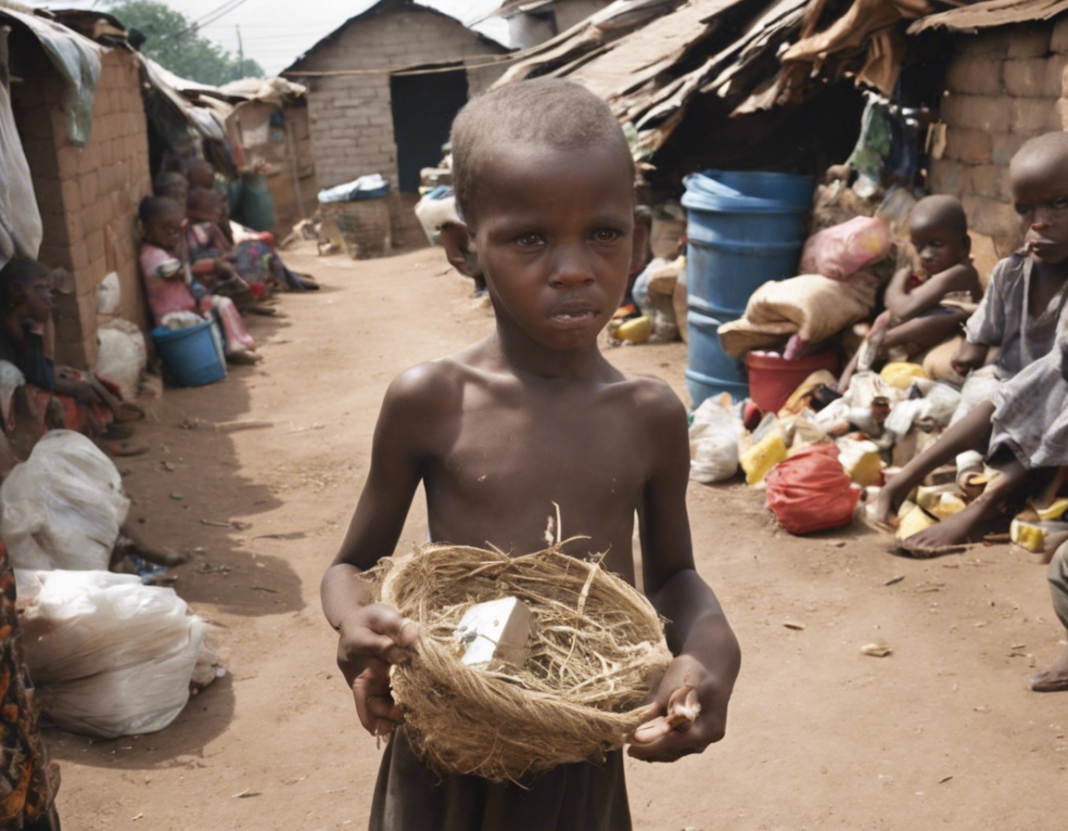
Poverty remains one of the most pressing issues facing our world today. Despite significant progress in many regions, over 700 million people still live in extreme poverty, surviving on less than $1.90 a day according to the World Bank. The eradication of poverty is at the core of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations, aiming to end poverty in all its forms by 2030. In this article, we will delve into the root causes of poverty, its impacts on individuals and societies, as well as strategies to alleviate poverty on a global scale.
Understanding Poverty
What is Poverty?
Poverty is a multifaceted phenomenon that goes beyond a lack of income. It encompasses inadequate access to basic needs such as food, water, shelter, healthcare, and education, as well as limited opportunities for social and economic mobility. Poverty can be categorized into absolute poverty, where individuals lack the basic necessities for survival, and relative poverty, which refers to a standard of living significantly below the average in a particular society.
Causes of Poverty
1. Inequality
Economic Inequality is a significant driver of poverty, with a small minority holding a disproportionate share of wealth and resources. This unequal distribution creates barriers for those at the bottom of the socioeconomic ladder to access opportunities for advancement.
2. Unemployment
Lack of Employment Opportunities is a common cause of poverty, as joblessness leads to income insecurity and financial instability. Structural issues such as automation, globalization, and economic downturns can exacerbate high rates of unemployment.
3. Lack of Education
Limited Access to Education perpetuates the cycle of poverty by restricting individuals from acquiring the skills and knowledge needed to secure well-paying jobs. Education is crucial for breaking the intergenerational transmission of poverty.
4. Poor Governance
Corruption and Ineffective Governance can drain resources from social programs intended to support those in need. Lack of transparency and accountability in government institutions hinders efforts to combat poverty effectively.
Impacts of Poverty
1. Health
Poverty is closely linked to Poor Health Outcomes, as limited access to healthcare services and nutritious food can lead to malnutrition, disease, and high mortality rates. Poverty significantly increases the risk of health issues such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria.
2. Education
Educational Opportunities are often limited for individuals living in poverty, perpetuating a cycle of low literacy rates and limited skill development. This lack of education hinders economic progress and social mobility for future generations.
3. Food Insecurity
Poverty is a primary driver of Food Insecurity, where individuals struggle to access an adequate and nutritious diet on a consistent basis. Malnutrition resulting from food insecurity can have long-term consequences on physical and cognitive development.
4. Social Exclusion
Poverty can lead to Social Exclusion, where individuals are marginalized from participating fully in society due to their economic status. This exclusion can result in discrimination, stigmatization, and limited access to social services and opportunities.
Strategies to Alleviate Poverty
1. Economic Empowerment
Promoting Economic Opportunities through job creation, skills training, and entrepreneurship support can empower individuals to generate sustainable income and break the cycle of poverty. Microfinance initiatives and access to credit can also enable individuals to start small businesses.
2. Social Safety Nets
Establishing Social Safety Nets such as cash transfer programs, food assistance, and healthcare subsidies can provide immediate relief to those living in poverty. These programs help address basic needs and prevent individuals from falling further into destitution.
3. Education and Skill Development
Investing in Education and Skill Development is crucial for equipping individuals with the tools needed to secure stable employment and improve their socioeconomic status. Scholarships, vocational training, and adult education programs can broaden opportunities for upward mobility.
4. Healthcare Access
Improving Access to Healthcare services is essential in combating the health repercussions of poverty. Universal healthcare coverage, community clinics, and health education programs can ensure that individuals living in poverty receive the medical attention they need.
5. Sustainable Development
Promoting Sustainable Development practices that prioritize environmental conservation, climate action, and equitable resource distribution can help address the root causes of poverty in the long term. Sustainable initiatives create opportunities for economic growth while safeguarding natural resources for future generations.
Conclusion
Addressing poverty is a complex global challenge that requires coordinated efforts from governments, civil society, and the private sector. By understanding the root causes of poverty, recognizing its impacts on individuals and societies, and implementing targeted strategies for alleviation, we can work towards a more equitable and sustainable world. Eradicating poverty is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic investment in building resilient and prosperous communities for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the different types of poverty?
Poverty can be categorized into absolute poverty, where individuals lack the basic necessities for survival, and relative poverty, which refers to a standard of living significantly below the average in a particular society.
2. How does poverty affect children?
Childhood poverty can have long-lasting impacts on physical and cognitive development, educational outcomes, and overall well-being. Children living in poverty are more likely to experience food insecurity, lack access to quality education, and face higher risks of health problems.
3. What role do governments play in poverty alleviation?
Governments play a critical role in poverty alleviation through the implementation of social welfare programs, economic policies that promote job creation, investments in education and healthcare, and the establishment of social safety nets to protect vulnerable populations.
4. How can individuals contribute to poverty alleviation efforts?
Individuals can contribute to poverty alleviation through donations to reputable charities, volunteering their time and skills to organizations working in impoverished communities, advocating for policy changes that address systemic inequalities, and supporting fair-trade and sustainable businesses.
5. What are some successful examples of poverty alleviation programs?
Programs such as Brazil’s Bolsa Familia, India’s Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), and Rwanda’s Girinka Programme have been successful in reducing poverty levels by providing cash transfers, employment opportunities, and livestock assets to disadvantaged populations.